What Materials Can an Electromagnetic Lifter Handle? – Industrial Lifting Solutions
September 2025 – Global – Efficient material handling is critical for modern industrial operations. Electromagnetic Lifters have become indispensable tools for safely and efficiently moving heavy ferrous materials. By understanding the types of materials they can handle, industrial buyers can maximize productivity in scrap yards, steel mills, recycling centers, and fabrication plants.
Key Applications of Electromagnetic Lifters
Electromagnetic lifters are versatile and widely used across industries:
Scrap Metal Recycling: Lifting steel sheets, scrap bars, and cut metal pieces.
Steel Mills & Foundries: Handling hot and cold billets, slabs, and ingots.
Auto Dismantling & ELV Centers: Transporting crushed vehicles, steel frames, and automotive components.
Ports, Yards & Logistics Terminals: Loading and unloading steel coils, sheets, and scrap metal.
Metal Fabrication & Processing Plants: Moving fabricated parts, cut sheets, and structural components.
Aluminum & Non-Ferrous Recycling: Handling aluminum plates, extrusions, and recycled materials.
Construction & Curtain Wall Companies: Lifting steel panels, beams, and heavy assemblies.
These applications demonstrate the lifter’s ability to enhance productivity, reduce manual labor, and improve workplace safety.
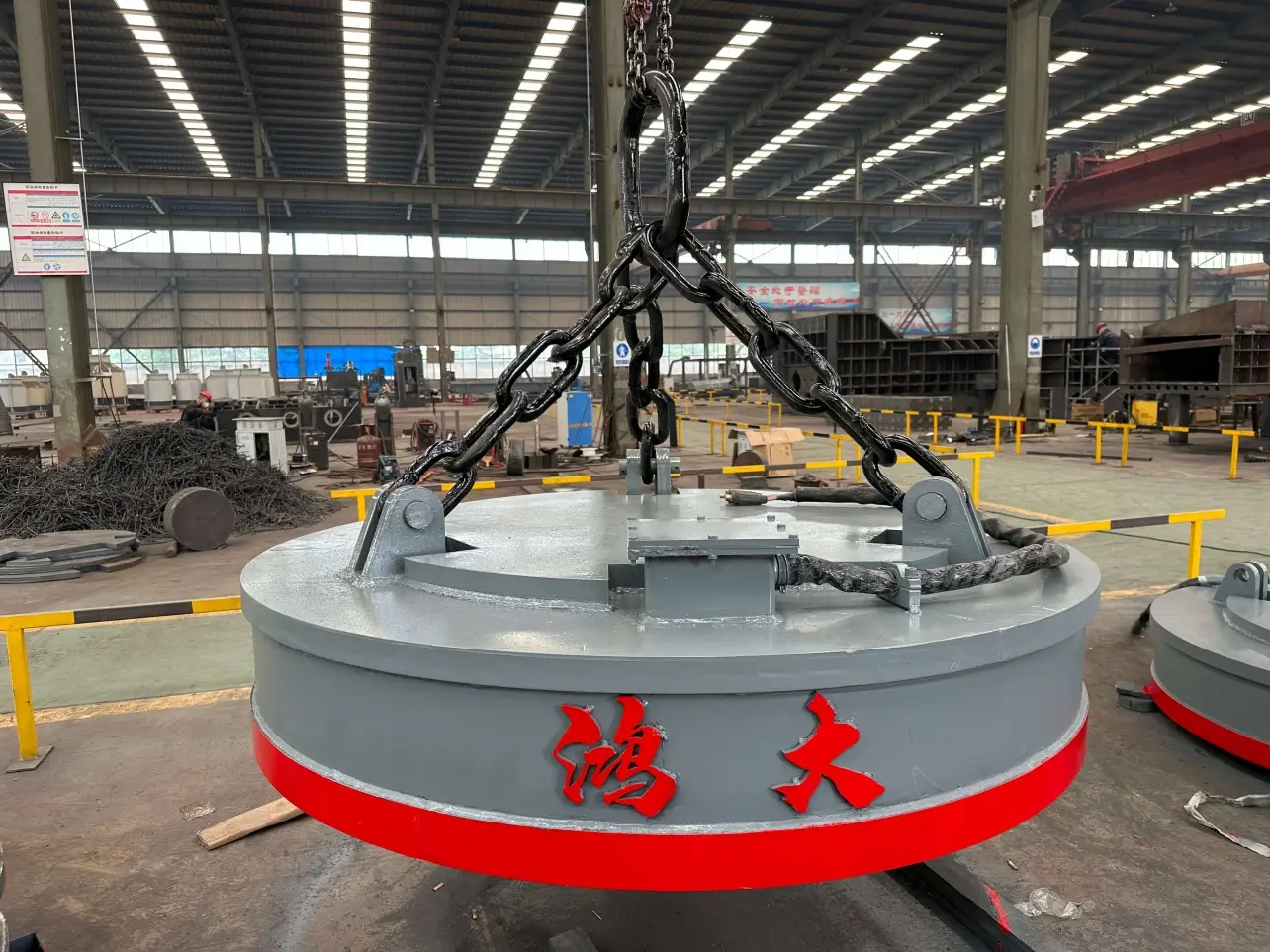

Technical Specifications of Electromagnetic Lifters
Electromagnetic lifters vary by design, capacity, and power source. Key features include:
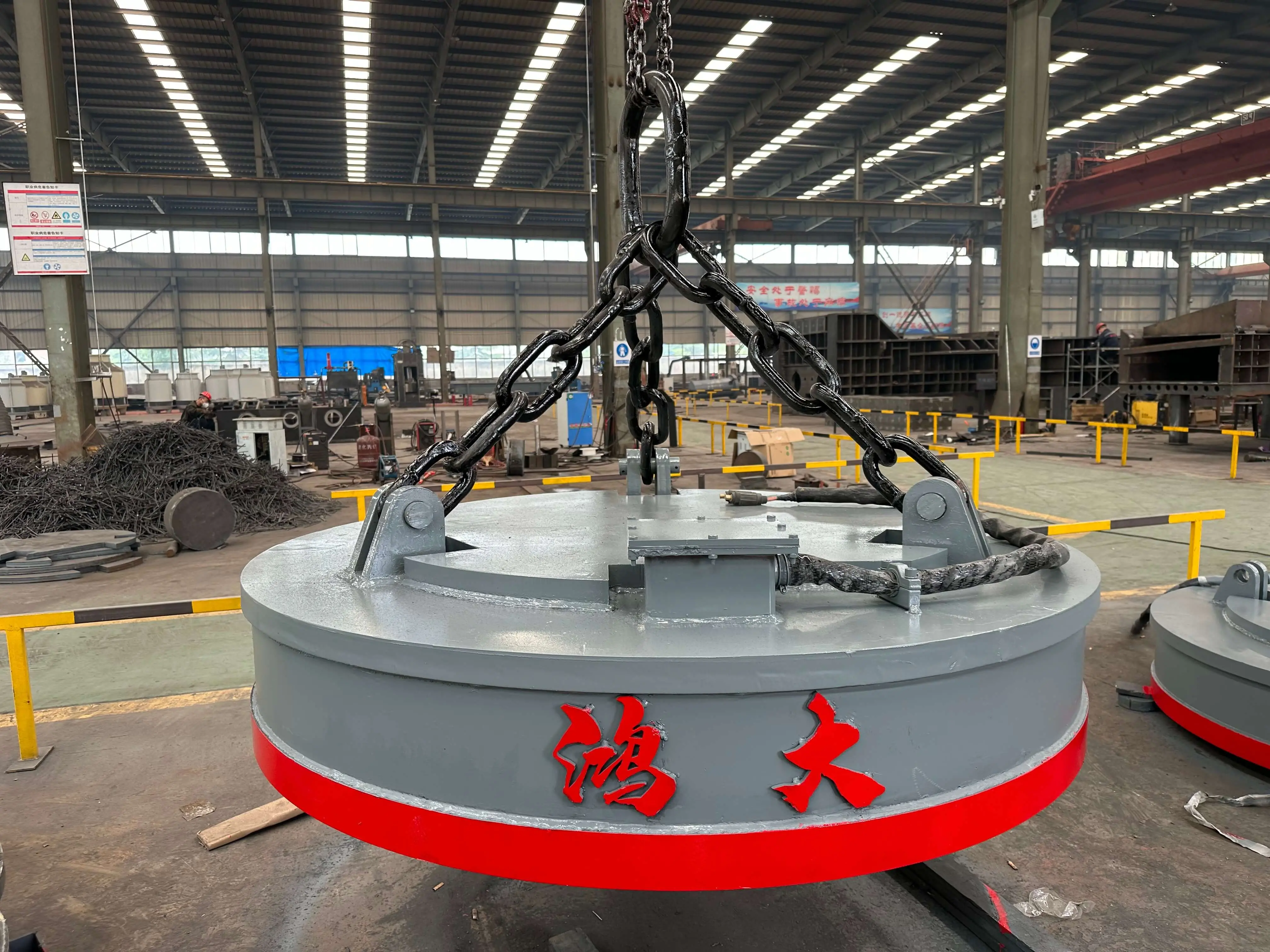
Lifting Capacity: 500 kg to 20+ tons depending on model
Power Source: AC, DC, or diesel-hybrid options for off-grid operations
Material Compatibility: Ferrous metals such as mild steel, stainless steel, iron, and certain alloyed steels
Control Options: Manual switches, remote controls, or PLC integration
Operation Modes: Continuous or pulse magnetization
Safety Features: Overload protection, emergency stop, anti-drop mechanisms
These features ensure reliability, safety, and precision in high-volume industrial operations.
How Electromagnetic Lifters Improve Operational Efficiency
Time-Saving: Rapid attachment and release streamline loading/unloading
Labor Reduction: Fewer workers needed for heavy material handling
Safety Enhancement: Minimizes risks associated with manual lifting
Versatility: Compatible with a variety of ferrous materials
Durability: Robust construction ensures long-term reliability
Real-World Customer Success Stories
Steel Mills: Reduced manual handling injuries by 40% using large-capacity electromagnets
Scrap Yards: Increased daily throughput by 30% while handling irregular scrap shapes
Auto Dismantlers: Improved workflow and storage optimization for compacted vehicle shells
According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global industrial lifting equipment market is projected to reach $27.4 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.3%, highlighting increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions like electromagnetic lifters.
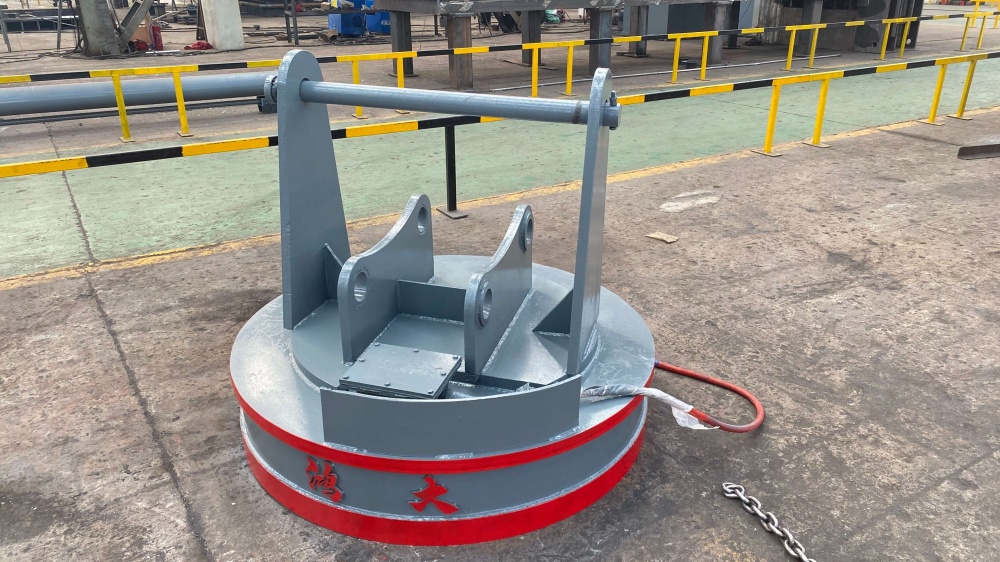

Choosing the Right Electromagnetic Lifter
Consider these factors when selecting a lifter:
Material Type: Magnetic strength must match material composition and thickness
Weight Capacity: Ensure safe handling of maximum load
Power Availability: AC, DC, or hybrid options
Operating Environment: Temperature, humidity, dust, or water exposure
Automation Needs: Manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated
Proper selection maximizes performance, safety, and ROI.
FAQ
Q1: What materials can an electromagnetic lifter handle?
A1: Primarily ferrous metals, including mild steel, stainless steel, iron, and certain alloyed steels. Non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper cannot be lifted with standard electromagnets.
Q2: How does an electromagnetic lifter work?
A2: An electromagnetic field generated by electric current creates magnetic force, allowing ferrous materials to attach. Cutting the current safely releases the load.
Q3: Can electromagnetic lifters be used outdoors?
A3: Yes, industrial-grade lifters are weatherproof, but it is important to consider dust protection and power supply availability.
Q4: How is safety ensured?
A4: Overload protection, emergency stop, proper load rating, and regular maintenance. Operators should be trained in handling procedures.